Opioid Overdose Crisis in America.
Introduction to the Opioid Overdose Crisis
America is facing a profound opioid crisis, overshadowing other public health issues with devastating consequences.
Scope and Impact of the Crisis
The opioid crisis claims an average of 130 lives daily in the United States, drastically reducing life expectancy.
Causes and Contributors
Explore the factors contributing to opioid addiction, including over-prescription of pain relievers and the rise of synthetic opioids.
Economic and Health Burden
The economic burden of opioid misuse in the US is estimated at $78.5 billion annually, encompassing healthcare costs, lost productivity, and more.
Facts and Statistics
Rise in Prescription Rates
Opioid prescriptions surged from 112 million to 282 million between 1992 and 2012, declining slightly to 236 million by 2017.
Impact on Overdose Deaths
About 68% of the 70,200 drug overdose deaths in 2017 were opioid-related, a stark increase from previous decades.
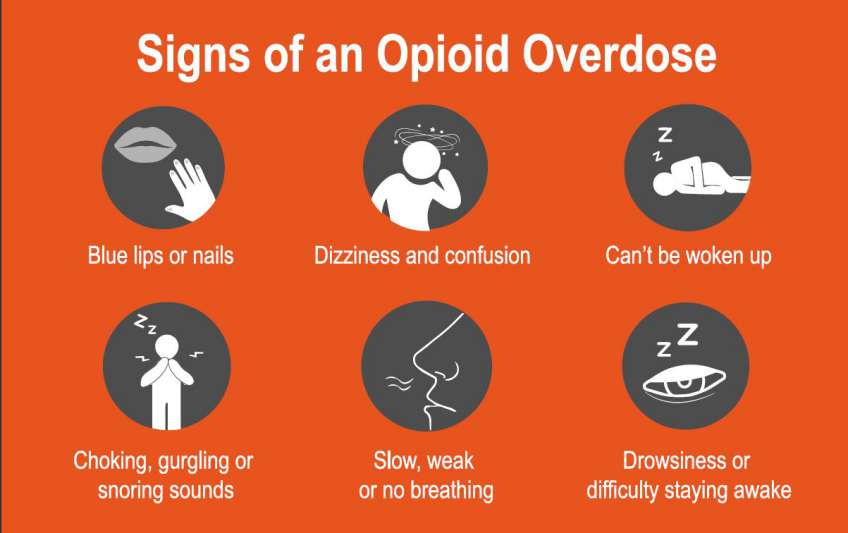
Misuse and Addiction Rates
Studies show that 21-29% of patients with chronic pain misuse prescription opioids, contributing to addiction rates.
Efforts to Combat the Crisis
Government Initiatives
The US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) is tackling the crisis through initiatives focusing on overdose-reversing drugs, treatment access, research, public health surveillance, and pain management improvements.
HEAL Initiative
Introduced by the NIH, the HEAL (Helping to End Addiction Long-term) Initiative aims to accelerate scientific solutions to the opioid crisis.
Conclusion: Moving Forward
Despite media attention deficits, the opioid crisis demands urgent attention and coordinated efforts to mitigate its devastating impact on American communities.
Share Your Insights
What are your thoughts on the opioid crisis and its management strategies? Share your perspectives and experiences.
Final Thoughts
Addressing the opioid overdose crisis requires continued collaboration and innovation across healthcare, research, and public policy domains.
These headings structure the content for better SEO and readability, focusing on key aspects of the opioid overdose crisis and efforts to address it in the United States.
- Published in Blog
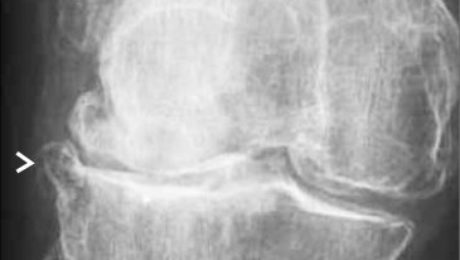
Autologous mesenchymal stem cell application for cartilage defect in recurrent patellar dislocation: A case report
Introduction
Recurrent patellar dislocation is characterized by repeated episodes of knee cap displacement, often resulting in cartilage lesions and chronic symptoms. Traditional management approaches often yield limited success, necessitating innovative treatments such as mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) therapy.
Case Presentation
Patient History and Examination
A 21-year-old male presented with left knee discomfort following recurrent patellar dislocations over ten years. Physical examination revealed anterior knee pain exacerbated by activities like stair climbing and exercise. Diagnostic imaging confirmed significant cartilage defects, classified as Grade 3 according to ICRS standards.

Surgical Intervention
The patient underwent arthroscopic microfracture and autologous bone marrow-derived MSCs implantation following Fulkerson osteotomy. Surgical procedures included lateral retinaculum release and tibial tubercle realignment to stabilize the patella.


Treatment Outcome
Postoperative Recovery
Post-surgery, the patient achieved full range of motion and began weight-bearing exercises. Eighteen months later, MSC implantation facilitated significant cartilage growth, improving International Knee Documentation Committee (IKDC) and Visual Analog Scale (VAS) scores.
Long-term Assessment
Two years post-MSC treatment, the patient reported no knee complaints and maintained full range of motion. MRI confirmed substantial cartilage regeneration in previously damaged areas.

Discussion
Challenges in Management
Recurrent patellar dislocations pose challenges due to high recurrence rates and associated cartilage damage. Treatment strategies like Fulkerson osteotomy combined with MSC therapy offer promising outcomes for severe cases.
Role of MSC Therapy
MSCs demonstrate potential in cartilage regeneration due to their chondrogenic differentiation capabilities and anti-inflammatory properties. This case highlights the efficacy of MSC therapy in managing extensive cartilage defects.
Conclusion
Combining Fulkerson osteotomy with MSC implantation represents a viable treatment option for chronic patellar instability and associated cartilage lesions. The integration of microfracture and MSC therapy supports significant cartilage regeneration and functional recovery.
- Published in Blog
Autologous micro-fragmented adipose tissue for the treatment of diffuse degenerative knee osteoarthritis: an update at 3 year follow-up
Background
The management of chondral disease poses challenges due to its poor healing potential. Biomechanical and biological changes can accelerate degeneration, leading to end-stage osteoarthritis (OA).
Conservative Therapies
Various conservative treatments are utilized before surgery, including non-pharmacological interventions and intra-articular therapies. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), particularly from adipose tissue, show promise in cartilage regeneration due to their anti-inflammatory and regenerative properties.
Methods
The study, approved by the Ethics Committee, involved 30 patients with diffuse degenerative chondral lesions treated with autologous micro-fragmented adipose tissue between January and December 2014. Clinical evaluations were conducted at 3 years post-treatment.
Findings
Of the 30 patients, 24 underwent associated surgeries, while 6 had arthroscopy alone. At 3 years, 23% of patients received additional treatments. No adverse events were reported.
Results
Patients not requiring additional treatments maintained outcomes observed at 1 year, with significant improvements in functional scores including Tegner Lysholm Knee, VAS pain, IKDC subjective, and total KOOS.
Discussion
The study demonstrates sustained benefits of autologous micro-fragmented adipose tissue in treating diffuse degenerative knee chondral lesions at mid-term follow-up, supporting its role as an adjunct in surgical procedures.
Conclusion
Micro-fragmented adipose tissue shows promise in mitigating chondral degeneration, warranting further investigation into its protective effects in knee OA management.
References.
- Ährlund-Richter L, De Luca M, Marshak DR, Munsie M, Veiga A, Rao M (2009) Isolation and production of cells suitable for human therapy: challenges ahead. Cell Stem Cell 4(1):20–26View ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Arcidiacono JA, Blair JW, Benton KA (2012) US Food and Drug Administration international collaborations for cellular therapy product regulation. Stem Cell Res Ther 3(5):1View ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Bonasia DE, Dettoni F, Sito G, Blonna D, Marmotti A, Bruzzone M, Castoldi F, Rossi R (2014) Medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy for medial compartment overload/arthritis in the varus knee: prognostic factors. Am J Sports Med 42(3):690–698View ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Caplan AI (2008) All MSCs are pericytes? Cell Stem Cell 3(3):229–230View ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Caplan AI, Correa D (2011) The MSC: an injury drugstore. Cell Stem Cell 9(1):11–15View ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Caplan AI, Dennis JE (2006) Mesenchymal stem cells as trophic mediators. J Cell Biochem 98(5):1076–1084View ArticleGoogle Scholar
- De Girolamo L, Kon E, Filardo G, Marmotti A, Soler F, Peretti G, Vannini F, Madry H, Chubinskaya S (2016) Regenerative approaches for the treatment of early OA. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 24(6):1826–1835View ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Pak J, Lee JH, Kartolo WA, Lee SH (2016) Cartilage regeneration in human with adipose tissue-derived stem cells: current status in clinical implications. Biomed Res Int 2016:4702674View ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Røtterud JH, Risberg MA, Engebretsen L, Årøen A (2012) Patients with focal full-thickness cartilage lesions benefit less from ACL reconstruction at 2–5 years follow-up. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 20(8):1533–1539View ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Ruetze M, Richter W (2014) Adipose-derived stromal cells for osteoarticular repair: trophic function versus stem cell activity. Expert Rev Mol Med 16:e9View ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Russo A, Condello V, Madonna V, Guerriero M, Zorzi C (2017) Autologous and micro-fragmented adipose tissue for the treatment of diffuse degenerative knee osteoarthritis. J Exp Orthop 4(1):33View ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Saithna A, Kundra R, Getgood A, Spalding T (2014) Opening wedge distal femoral varus osteotomy for lateral compartment osteoarthritis in the valgus knee. Knee 21(1):172–175View ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Sensebé L, Bourin P, Tarte K (2010) Good manufacturing practices production of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells. Hum Gene Ther 22(1):19–26View ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Su X, Li C, Liao W, Liu J, Zhang H, Li J, Li Z (2018) Comparison of arthroscopic and conservative treatments for knee osteoarthritis: a 5-year retrospective comparative study. Arthroscopy 34(3):652–659View ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Verdonk R, Madry H, Shabshin N, Dirisamer F, Peretti GM, Pujol N, Spalding T, Verdonk P, Seil R, Condello V (2016) The role of meniscal tissue in joint protection in early osteoarthritis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 24(6):1763–1774View ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Published in Blog
Stem Cells Offer Hope for Hair Growth
Introduction to Hair Follicle Stem Cells
Explore the role of hair follicle stem cells in the natural hair growth cycle and their significance in hair regeneration research.
UCLA Research Discovery
Highlight the groundbreaking research by Heather Christofk, PhD, and William Lowry, PhD, revealing new methods to activate hair follicle stem cells for promoting hair growth.
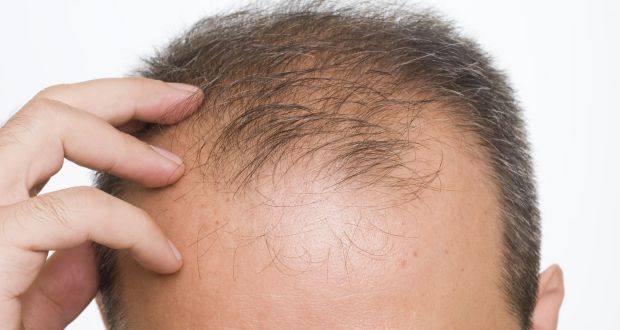
Understanding Hair Loss Factors
Discuss common causes of hair loss such as baldness, alopecia, hormonal imbalances, stress, aging, and chemotherapy, emphasizing the need for effective treatments.
Mechanisms of Hair Follicle Stem Cell Activation
Metabolic Pathways
Detail how hair follicle stem cell metabolism, particularly the production of lactate, plays a crucial role in stimulating hair growth.
Genetic Studies in Mice
Summarize the genetic studies in mice that demonstrated the impact of lactate production on hair follicle stem cell activation and hair cycle acceleration.
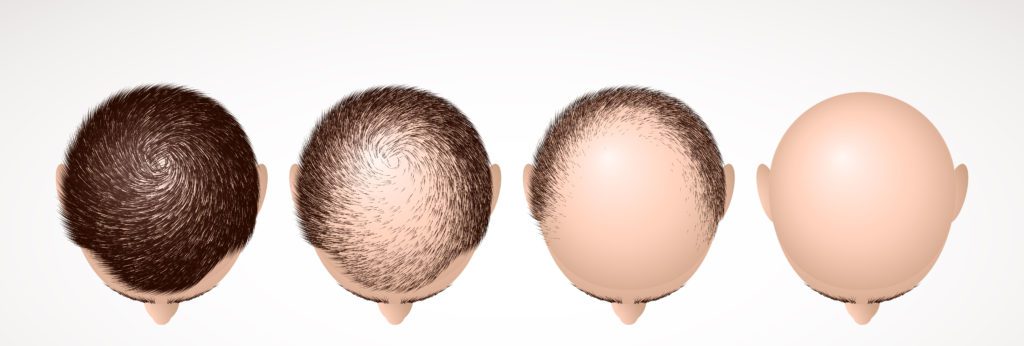
Drugs for Hair Growth Promotion
RCGD423: JAK-Stat Activation
Explain the role of RCGD423 in activating the JAK-Stat pathway, leading to increased lactate production and enhanced hair follicle stem cell activity.
UK5099: Mitochondrial Blockade
Discuss how UK5099 blocks pyruvate entry into mitochondria, thereby promoting lactate production and accelerating hair growth in experimental models.
Clinical Implications and Future Research
Potential Therapeutic Applications
Summarize the significance of UCLA’s research in advancing our understanding of hair follicle stem cells and potential treatments for hair loss disorders.
Explore the potential of JAK-Stat pathway activators and mitochondrial blockers in developing new drugs for treating hair loss disorders in humans.
Future Directions in Hair Regeneration Research
Highlight ongoing and future research directions aimed at translating these findings into clinical applications for patients suffering from hair loss.
Conclusion: Advances in Hair Regeneration Science
References
Ensure comprehensive citations of the original research publication and related studies supporting the efficacy of lactate-driven mechanisms in hair follicle stem cell activation.
These headings and optimizations aim to structure the article effectively for improved SEO and readability, focusing on key aspects of the UCLA research findings, mechanisms of hair growth, and potential therapeutic implications for treating hair loss disorders.
- Published in Blog
Which Works Better, Viscosupplementation, or Platelet Rich Plasma?
Understanding Viscosupplementation (Hyaluronic Acid)
Explore the mechanism and benefits of Hyaluronic Acid injections, FDA-approved for knee arthritis treatment but also used off-label for other joints.
Efficacy and Evidence of Viscosupplementation
Highlight the results from systematic reviews and randomized controlled trials supporting the effectiveness of Hyaluronic Acid in reducing pain and improving joint function.
Introduction to Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
Discuss PRP therapy, its composition rich in platelets and growth factors, and its applications beyond arthritis treatment, including tendon injuries and potential uses in other medical fields.
Comparison of Effectiveness: Viscosupplementation vs. PRP
Clinical Studies and Comparative Effectiveness
Summarize findings from studies comparing the efficacy of PRP and Hyaluronic Acid injections in managing arthritis pain and improving joint function.
FDA Approval and Regulatory Status
Regulatory Considerations for Treatment
Discuss the FDA approval status of Hyaluronic Acid for knee arthritis versus the off-label use of PRP, and its implications for treatment options and insurance coverage.
Safety Profile and Cost Comparison
Safety and Economic Considerations
Compare the safety profiles of PRP and Hyaluronic Acid, including risks of infection and cost-effectiveness considerations for patients.
Choosing Between HA and PRP: Factors to Consider
Patient-Specific Decision Making
Guide patients on factors influencing the choice between HA and PRP based on efficacy, safety, regulatory status, and cost.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Treatment
Summarize the advantages and considerations of both Viscosupplementation (HA) and PRP therapies for arthritis pain management, aiding in informed treatment decisions.
References
Ensure comprehensive citations of systematic reviews, clinical trials, and regulatory information supporting the comparison between HA and PRP therapies.

- Published in Blog
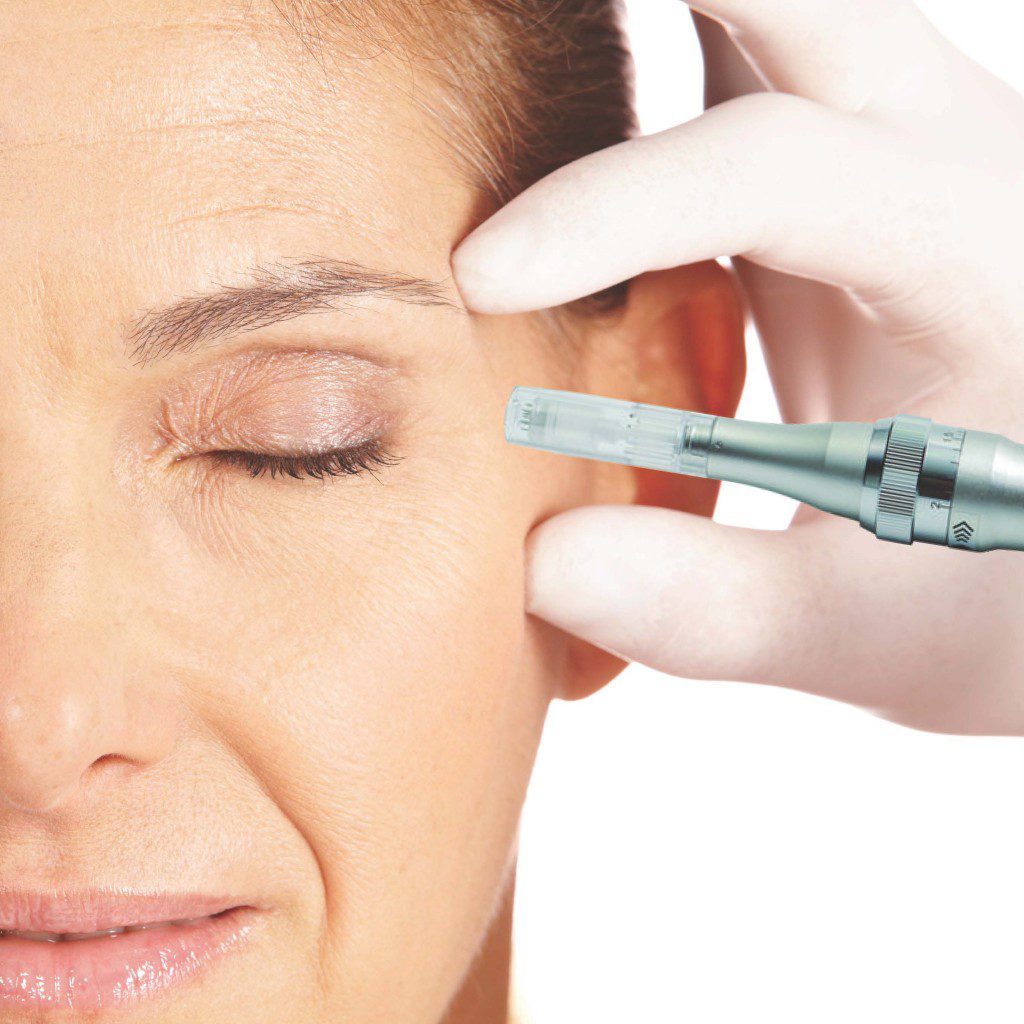
How Regenerative Microneedling Can Help Rejuvenate Skin?
Understanding Microneedling for Acne Scars
Explore how microneedling initiates collagen synthesis and aids in skin healing, particularly effective for treating acne scars.
The Role of Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) in Skin Rejuvenation
Highlight the benefits of PRP therapy in conjunction with microneedling for enhancing skin regeneration and reducing scars.
Scientific Evidence: Effectiveness of PRP with Microneedling
Study by Department of Dermatology, Venereology, and Leprosy
Discuss findings from studies evaluating the effectiveness and safety of PRP combined with microneedling for acne scar treatment.
Mechanism of Action: How Microneedling Works
Initiating Collagen Synthesis and Healing
Explain the process of microneedling in triggering the body’s healing response through controlled micro-injuries and the delivery of growth factors.
Clinical Results: PRP vs. Distilled Water in Microneedling
Comparative Study Outcomes
Summarize results showing the superior efficacy of PRP compared to distilled water in improving acne scars based on clinical trials.
Patient Testimonials and Success Stories
Real-life Experiences
Share patient success stories and testimonials demonstrating the effectiveness of PRP with microneedling in improving skin texture and reducing scars.
Integrating PRP Therapy into Dermatology Practice
Implementation and Considerations
Guide dermatologists on integrating PRP therapy into their practice for effective acne scar management and patient satisfaction.
Conclusion: Advantages of PRP in Skin Rejuvenation
Summarize the benefits of combining PRP with microneedling as an effective treatment option for patients seeking skin rejuvenation and scar reduction.
References
Ensure comprehensive citations of studies and research supporting the efficacy and safety of PRP with microneedling in dermatological treatments.
- Published in Blog
What’s all the fuss about Regenerative Medicine?
Understanding Regenerative Medicine
Explore the concept of regenerative medicine and its role in healing various ailments using the body’s natural processes.
Benefits of Regenerative Medicine
Discover why patients are turning to regenerative medicine for non-invasive treatments with minimal side effects.
How Regenerative Medicine Works
Extraction and Application of Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP)
Explain the process of obtaining PRP from a patient’s own blood or tissues and its application to promote healing.
Patient Experiences with Regenerative Medicine
Testimonials and Success Stories
Share real-life accounts of patients who have benefited from regenerative medicine treatments, highlighting their positive outcomes.
Future of Regenerative Medicine in Healthcare
Predictions and Trends
Discuss the potential growth and importance of regenerative medicine in future healthcare practices, likening its impact to groundbreaking medical advancements like penicillin.
Training and Implementation in Medical Practice
Integrating Regenerative Medicine
Explore how physicians are incorporating regenerative medicine into their practice through specialized training courses to enhance patient care.
Comparing Regenerative Medicine to Traditional Treatments

Advantages Over Conventional Medicine
Highlight the advantages of regenerative medicine over traditional medical approaches in terms of effectiveness and patient satisfaction.
Conclusion: Embracing Regenerative Medicine
Summarize the potential of regenerative medicine to revolutionize healthcare by offering effective, non-invasive treatments with fewer side effects.
References
Ensure comprehensive citations and references to support claims and information presented about regenerative medicine.
- Published in Blog
Platelet-Rich Plasma Vs Stem Cell Therapy: Who’s Bad?
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy Explained
Learn how PRP utilizes natural healing mechanisms to enhance tissue repair and manage joint issues like arthritis.
Stem Cell Therapy: A Revolutionary Approach
Explore the potential of stem cell therapy in regenerative medicine and its applications in treating various orthopedic conditions.
Comparing PRP and Stem Cell Therapy
Mechanisms and Applications
Differentiate between PRP and stem cell therapy, highlighting their unique roles in healing and tissue regeneration.
Benefits of Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
Advantages Over Stem Cell Therapy
Discuss the specific benefits of PRP, such as safety and simplicity, compared to more complex stem cell procedures.
Risks and Considerations with Stem Cell Therapy
Potential Drawbacks
Examine the risks associated with stem cell therapy, including concerns about uncontrolled growth and immune responses.
Conditions Treated with Stem Cell Therapy
Orthopedic Applications
Explore common orthopedic conditions effectively treated with stem cell therapy, including arthritis and joint injuries.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Treatment Option
Making Informed Decisions
Summarize key points to help patients and healthcare providers make informed choices between PRP and stem cell therapy.
Future of Regenerative Technologies
Trends and Innovations
Look ahead to the future of regenerative medicine, discussing advancements and potential developments in both PRP and stem cell therapies.
References and Further Reading
Ensure comprehensive citations and references to support claims and information presented about PRP and stem cell therapies.
- Published in Blog
Platelet-Rich Plasma Stays Quietly Popular Despite Neglect
Introduction
FRIDAY, 27 APRIL 2018 / PUBLISHED IN BLOG
Fact: PRP Treatments in High Demand
According to research, PRP treatments are one of the most in-demand treatments available in healthcare. This is impressive considering the following:
- PRP is not supported by the medical industry. No big pharma funding on extensive research or marketing. No medical associations lobbying to increase its awareness.
- PRP is shunned by the insurance companies. No reimbursements from them. So getting patients to pay is difficult, especially for a treatment that’s relatively “unproven” like this.
- The cost of PRP treatments is actually rising. In 2006, you could get a PRP treatment for $450. Today it costs $800. The cheapest we’ve seen is $650. The prices are still robust as demand keeps up.
The Future Potential of PRP
We believe the best of PRP is not even here yet. We’re just one breakthrough study away from exploding into mainstream hospitals and clinics. We see the biggest growth in Platelet-Rich Plasma happening in Asia.
Strongly Based on Fundamental Healing Theory
The growth can be attributed to PRP’s fundamental healing property. More platelets. More growth factors and cytokines. And therefore more healing. It’s as simple as that. And no one can argue this fact.
Our body’s natural healing mechanism operates with 150,000/ul-350,000/ul platelets in blood. Using Platelet-Rich Plasma means this number is amplified by 3X to 5X. How can this not translate into better healing?
Believe it or not, the best orthopedic doctors use Platelet-Rich Plasma regularly.
PRP’s Applications and Effectiveness
PRP can be used to promote healing of injured tendons, ligaments, muscles, and joints and can be applied to various musculoskeletal problems. They conduct regular studies to test its effectiveness.
Key Study on PRP and Chronic Low Back Pain
One landmark study involved double-blind randomized controlled trials to see the effect of PRP on patients with chronic low back pain caused by torn discs. The study outcome says 60% of the patients felt significant improvements. Some were cured.
Different Variants of Platelet-Rich Plasma
So far, there are the following types of PRP variants:
- Plasma Rich in Growth Factors (PRGF)
- Plasma Rich in Platelets and Growth Factors (PRPGF)
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP); Platelet Poor Plasma (PPP)
- Plasma Rich in Platelets and Rich in Leukocytes (LR-PRP)
- Plasma Rich in Platelets and Poor in Leukocytes (LP-PRP)
- Platelet-Rich Fibrin Matrix (PRFM)
All of them involve plasmapheresis — the two-stage centrifugation process to separate platelets from blood. However, what happens after that can be different. The industry hasn’t found its middle ground as to which variant to be standardized. We believe the confusion will clear up in 3-5 years.
Bio-Factors at Play in PRP
No matter which variant you end up using, the bio-factors at play are the following:
- Growth factors: TGF-B, PDGF, IGF-I, II, FGF, EGF, VEGF, ECGF
- Adhesive proteins: Fibrinogen, Fibronectin, Vitronectin, Thrombospondin-1
- Clotting & Anti-Clotting factors: Proteins, Antithrombin, Plasminogen, Proteases, Antiproteases
How Platelet-Rich Plasma Actually Works
Why is the treatment commonly used for wound healing and pain management? The answer is because the platelets’ main job is to aid coagulation, act as a biological glue, and support stem or primary cell migration. In addition, it also helps in restoring hyaluronic acid and accelerates the synthesis of collagen and glycosaminoglycans, increasing the cartilage matrix.
Not only that, the platelets are delivered in a clot, which means it can immediately act as a scaffold to enable the healing process. 95% of the bio-active proteins are released within 1 hour of injecting Platelet-Rich Plasma. The platelets continue to release growth factors for 7-10 days. Thus it’s recommended to re-inject PRP every 7 days.
Patient Perspective on PRP Costs
Why are patients coughing up their hard-earned money for this?
This reminds me of hundreds of thousands of PRP treatments paid from patients’ own pockets even though they’ve been paying for years to get covered by their respective insurance providers. In 2015, PRP costs were anywhere between $600 and $800 per site per treatment. And most patients go for repeated treatments. So why were they forking up their hard-earned money if the treatment was not working? Weren’t there any better alternatives under the “coverage” of their insurance provider? The answer is 1) the treatment works. 2) there’s nothing else out there that’s as natural and side-effect-free as PRP.
PRP and Osteoarthritis
Consider the case of osteoarthritis. 27 million Americans are impacted by it. 33.6% of people older than 65 are victims. All of them experience gradual degeneration of cartilage and bones — they lose roughly 5% of cartilage per year. Yet, our medical industry doesn’t have a fix to stop it.
However, when doctors started doing PRP treatments for their osteoarthritis patients, they found a large majority of them had no further cartilage loss. To me, it means we should make PRP treatments the default first-line treatment for osteoarthritis across the country.
PRP in Hair Loss and Cosmetic Applications
Another huge market is hair loss and cosmetic facial applications. I know there are many people who believe PRP doesn’t work for hair. Here’s what one of the Platelet-Rich Plasma studies found were the effect of the treatment on hair loss.
“Hair loss reduced and at 3 months it reached normal levels. Hair density reached a peak at 3 months (170.70 ± 37.81, P < 0.001). At 6 months and at 1 year, it was significantly increased, 156.25 ± 37.75 (P < 0.001) and 153.70 ± 39.92 (P < 0.001) respectively, comparing to baseline. Patients were satisfied with a mean result rating of 7.1 on a scale of 1-10. No remarkable adverse effects were noted.”
I’ll take that. That’s me getting PRP for hair.
PRP Market Growth
The PRP market is expected to hit $126 million in 2016. That number looks paltry. But that’s a 180% increase over the 2009 figure of $45 million.
Consider this. Just for osteoarthritis alone, if all the 27 million Americans receive 1 PRP shot a year at a conservative $400 per treatment, it would be a market of $10 billion. And that’s one condition out of the many that Platelet-Rich Plasma injections are proven to work.
PRP and Tennis Elbow
Another condition that PRP is known to work very well is Tennis Elbow. It affects on average 1% to 3% of the overall population. That number is as high as 50% among tennis players.
Insurance Coverage and PRP
Just getting Platelet-Rich Plasma covered by insurance will unleash the market big time and will help heal millions of patients naturally, more effectively.
Oh ya, that means the insurance companies will have to pay more. Why would they?
Potential Savings for Insurance Companies
HOWEVER, if this treatment could reduce further expensive intervention like surgery, then it may actually be a blessing for the insurance guys in terms of savings. One surgery avoided by a patient through the right intervention through PRP treatments will save the insurance companies at least $25,000. Now, that’s a win-win for both patients and insurance.
I believe it’s a matter of time before insurance companies start realizing their folly of not supporting this treatment.
PRP Still Considered “Unproven”
After all is said and done, it’s still “unproven.” The problem with PRP is that it can be used for just about everything, which is a good problem to have until healthcare officials (and insurance companies) start realizing that people are going to misuse it.
So it’s classified as unproven. The VAST scope of the treatment calls for urgent structure and guidelines. There are some 20+ conditions where researchers have found it “helps” in one way or another. It’s a daunting task to prove its efficiency in all the areas. Nevertheless, we’ll get there. Though we’ll need a lot of funding for that.
Need for Standardization
And yes, we need to standardize the procedure. As well as come up with optimized protocols for each condition. Someone needs to take initiative on that. We’re counting on independent doctors and medical institutions. The big pharma won’t jump in because what’s in it for them, right?
Simplicity and Accessibility of PRP
It’s so simple, you’d be an idiot not to try it. You only need a vacuum blood harvesting tube like what we offer here, a centrifuge with an adapter for the tube, pipettes, and 10ml ampules of 10% calcium chloride.
The only complexity comes from not following a standard PRP system. Because the final platelet count can depend on a variety of factors like the initial volume of blood, the technique used, and the relative concentration of WBC and/or RBC. As well as on the patient’s side, there are factors such as age.
- Published in Blog
The Growth Factor Showdown: Plasma Vs Fibrin
WEDNESDAY, 25 APRIL 2018 / PUBLISHED IN BLOG
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) and Platelet-Rich Fibrin (PRF) have been the subject of numerous speculations regarding their efficacy in facilitating angiogenesis, hemostasis, osteogenesis, and bone growth. The primary reason these platelet products are effective is due to the growth factors they carry. Let’s delve into the specific roles of these growth factors in the healing process.
Growth Factors in Platelet-Rich Plasma
These growth factors play vital roles in PRP and contribute significantly to the healing process:
Platelet-Derived Growth Factor (PDGF)
Regulates cell growth and division, especially in blood vessels, making it crucial for blood vessel reproduction.
Transforming Growth Factor Beta (TGF-β)
Responsible for overall cell proliferation, differentiation, and various other cellular functions.
Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF)
Plays a key role in wound healing and embryonic development, influencing the proliferation and differentiation of specialized cells and tissues.
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF)
Essential for vasculogenesis and angiogenesis, VEGF restores oxygen supply to cells when it is inadequate and helps create new blood vessels after injury.
Keratinocyte Growth Factor (KGF)
Found during the epithelialization phase of wound healing, KGF stimulates the formation of epithelium immediately after a wound or injury occurs.
Connective Tissue Growth Factor (CTGF)
Functions in cell adhesion, migration, proliferation, angiogenesis, skeletal development, and tissue wound repair.
Platelet-Rich Plasma Rules
A recent study suggests that PRP and its gelled cousin, PRF, differ significantly in the release of these growth factors, which can affect the healing outcome. The study concludes that:
PRP releases significantly higher proteins at earlier time points, which is beneficial for short-term effects.
PRF shows a continual and steady release of growth factors over a 10-day period, making it more beneficial for long-term healing.
Advantages of Platelet-Rich Fibrin Over Platelet-Rich Plasma
PRF has some notable advantages over PRP, including:
- It doesn’t require thrombin and anticoagulants.
- It results in better healing due to its slow polymerization process.
- It aids in hemostasis.
How Platelet-Rich Plasma Differs from Platelet-Rich Fibrin
Platelet-Rich Plasma is produced using a double spin method: a hard spin to separate red blood cells from everything else in the autologous blood, followed by a soft spin to separate the platelets and white blood cells, resulting in PRP, Platelet-Poor Plasma (PPP), and Red Blood Cells.
Platelet-Rich Fibrin is created using a newer method. After the first centrifugation, the middle layer is taken, containing fewer platelets but more clotting factors. This gradually forms into a fibrin network that traps cytokines and is then centrifuged again to result in PRF, a fibrin layer containing platelets and plasma.
What Matters in Healing
When it comes to accelerating healing, the immediate availability of growth factors and cytokines is crucial. PRP may be more effective in this regard due to its immediate release of growth factors, allowing for repeated injections for additional healing factors just days after the initial injection.
Conclusion
Platelet-derived products are still in their infancy. Despite their potential benefits, more research is needed to fully understand their capabilities. If you’re a physician using any or both of these products, we encourage you to share your experiences with us through our contact form.
- Published in Blog